|
|
|
|
Family: Sapotaceae
Star-Apple, more... (es: caimito)
|
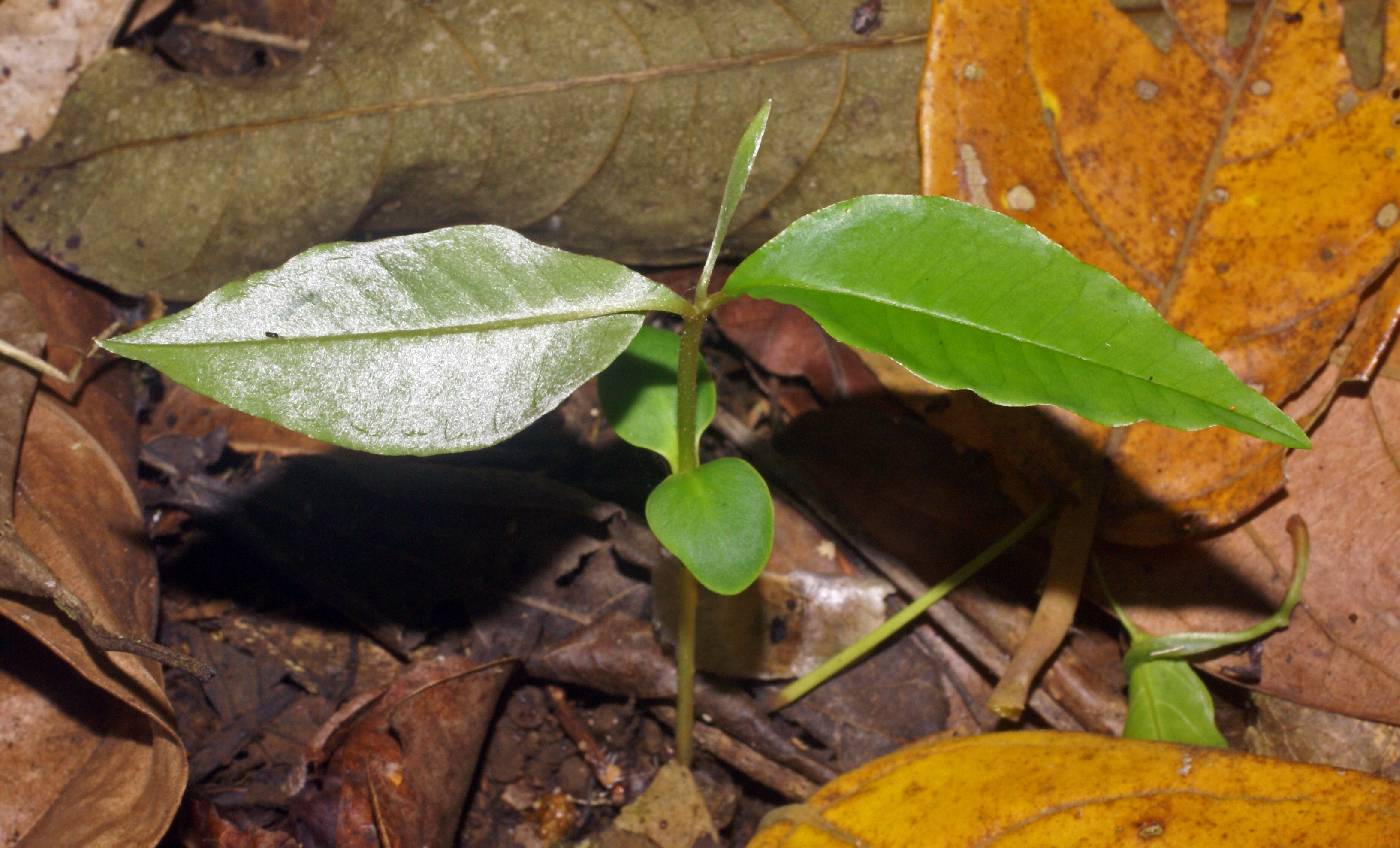
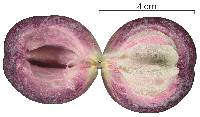
Description: Large forest tree, sometimes with a wide crown emerging above the main canopy. Trunk is slightly buttressed or irregular when large. Leaves are alternate, arranged regularly along branches, in a flat plane. The underside of the leaves is a striking, velvety, somewhat iridescent red, created by dense, soft hair. The twig zig-zags between leaves (like the Annonaceae), and also has soft, red pubescence. Like all Sapotaceae, broken leaves, or cut bark, produces dripping, white latex. Reproduction: Flowers... Fruits are large, plum-sized or larger, bluish, with a soft flesh that has a great, spicy flavor. Monkeys take them. Distribution: Found frequently in forests near Panama City, near Gamboa, and on Barro Colorado, where it is conspicuous but not especially numerous in the old-growth. Present, but rare in Soberania and Sherman, and not known in the wetter or higher elevation forests of Santa Rita or the mountains. Occasionally found outside the forest, but mostly a forest tree. Croat says this tree was introduced from the Caribbean; if so, it must have been brought several thousand years ago, given its frequent in mature forest and scarcity in settlements and farmland. Similar Species: With a leaf in hand, this species should not be confused - the other leaves with red undersides have a much different texture. Only LK2 luehse Luehea seemannii LK2 of the red-leaved group is a tall tree, and it can be mistaken for caimito at a distance, or if leaves are not carefully checked. Uses: The fruit is popular, and can be purchased that the agriculture market in Panama City. Descripción: Árbol de 10 a 25 m de alto. Copa umbelada y con follaje lustroso. Tronco con raíces tablares pequeñas en la base. Corteza exterior gris y fisurada, a veces exfoliante en láminas pequeñas. El desprendimiento de cualquier parte de la planta produce el flujo de una savia lechosa. Hojas simples y alternas, de 6-14 x 3-5 cm, elípticas, con ápice acuminado, bordes enteros y base obtusa. Las hojas tienen el haz verde oscuro y el envés marrón castaño y brillante. Pecíolo de 0.8-2 cm de largo y acanalado en la parte superior. Flores cremas o amarillentas y en fascículos axilares. Frutos en bayas globosas, de 4-7 cm de largo, verdes, tornándose rojos, morados o negros al madurar. Semillas con una cicatriz longitudinal. Datos Ecológicos: La especie crece a bajas elevaciones, en lugares secos o húmedos de todo el país. Común y fácil de observar en fincas a orillas de los ríos en áreas secas del Pacífico. Florece y fructifica de julio a marzo. Las flores son visitadas por abejas y otros insectos. Las semillas son dispersadas por animales. Especies Parecidas: A menudo se confunde con LK chr2ar Chrysophyllum argenteum LK2 , pero en C. argenteum las hojas no tienen el envés marrón castaño. También se puede confundir con LK luehse Luehea seemannii LK2 , pero en L. seemannii las hojas tienen los bordes dentados. Usos: La madera es empleada en construcciones locales, postes, muebles y mangos de herramientas. La pulpa de los frutos maduros es comestible y muy dulce. El árbol se utiliza con fines ornamentales en parques y avenidas. Tree, to 20 (25) m tall, ca 70 cm dbh; bark with white latex; wood pinkish, hard, heavy; branchlets and petioles densely brown-sericeous. Petioles 9-16 mm long; blades elliptic, acute or more often abruptly acuminate at apex, obtuse at base, 6.5-12 cm long, 3.5-6 cm wide, glabrous above except on midrib, densely brown-sericeous below, the midrib sunken above; major veins in 15-30 pairs, scarcely more prominent than the secondary lateral veins, forming an obscure collecting vein near margin. Fascicles axillary; pedicels ca 1 cm long; flowers cream-colored, numerous; sepals 5, ca 1.5 mm long; pedicels and outside of sepals densely brown-sericeous; corolla mostly 5-lobed about halfway, ca 4 mm long, sericeous outside; stamens equaling, opposite, and attached to corolla lobes, included; style to 0.5 mm long; stigma with 7-12 marginal lobes. Berries purple, subglobose, 5-10 cm diam; seeds several, oblique-obovate, flattened, to 2.5 cm long, the testa hard, lustrous. Croat 4630, Foster 1221. Rare in the old forest; known also from the Laboratory Clearing and from the shore of Bat Cove. Flowers from July to September. The fruits mature during the dry season of the following year. |
|
|
|