|
|
|
|
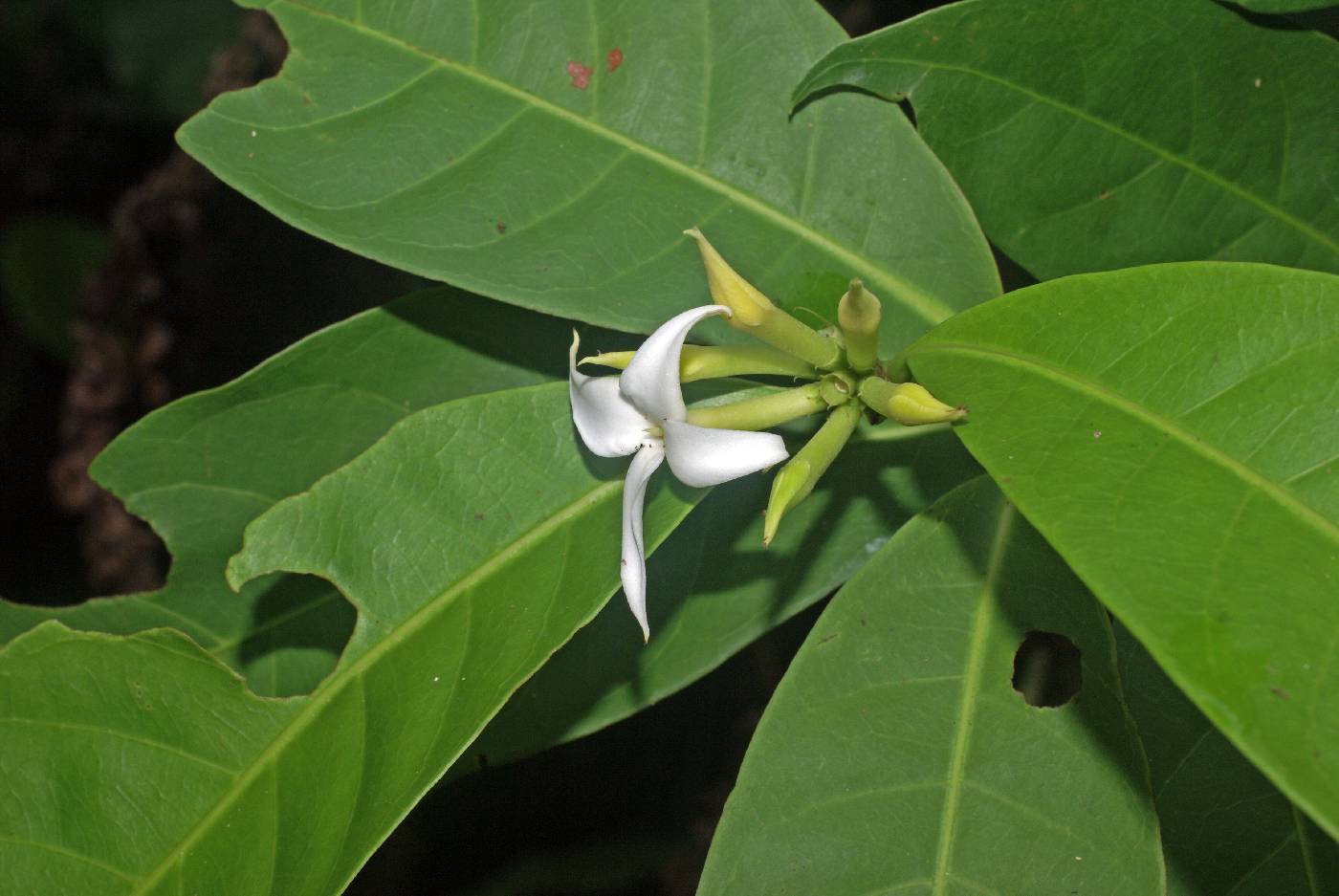
Family: Rubiaceae
guayabito de monte, more...trompito
|
Description: A forest treelet, not more than 7 m tall, with a stem often branching near the base and light brown bark. Leaves are simple, opposite, pointed at the tip but rounded at the base. The petiole is short with a slight channel running its length on the upper surface. There are usually domatia visible on the There are usually tiny pits (called domatia) visible on the underside of the leaf, at the axils between the primary and secondary veins. Stipules are green, leaflike, a few millimeters long, pointed, in a pair at the base of each leaf pair; they form a tube around the branchlet. Reproduction: The white flowers are fairly large and produced from April to July. The fruits is a berry that matures yellowish or darker, with a green crown at the apex (remnants of the flower); dispersed by birds. Distribution: Widespread in the understory of lowland forests along the Canal, but much more common near the Pacific coast. Moderately common around Gamboa, somewhat less so at Soberania and Barro Colorado, and rare at Sherman. Only seen inside the forest, never along roads or in towns. Similar Species: Since the paired stipules are usually present at the base of the opposite leaves, this is readily recognized as Rubiaceae, but there are a lot of Rubiaceae. Some Psychotria, such as LK psycma P. marginata, LK2 have similar leaves with domatia. You have to study details of the leaves and stipules. Uses: The fruit is edible, but with little pulp. The small stems are sometimes used for making tools or as firewood. Descripción: Árbol de 2 a 7 m de alto. Tronco con la corteza exterior marrón. Hojas simples y opuestas, de 7-20 x 2-6 cm, oblongas o lanceoladas, con ápice acuminado, bordes enteros y base obtusa. Las hojas a veces presentan domacios en las axilas de las nervaduras del envés. Estípulas persistentes, envolviendo las ramitas en los ápices. Pecíolo de 0.5-1 cm de largo y acanalado en la parte superior. La especie es dioica. Flores solitarias, blancas y aromáticas. Fruto globoso, de 2-4 cm de diámetro, verdes y con una estructura en forma de corona en la punta, tornándose amarillos, negros o blancos al madurar. Datos Ecológicos: La especie crece a bajas elevaciones, en bosques secos o húmedos de todo el país. Común en matorrales y bosques secundarios secos. Florece y fructifica durante todo el año, principalmente de abril a octubre. Las flores son visitadas por insectos y colibríes. Especies Parecidas: A menudo se confunde con LK vismbi Vismia billbergiana LK2 , pero V. billbergiana presenta savia anaranjada y no tiene estípulas. También se puede confundir con LK alibga Cordiera garapatica LK2 , pero en C. garapatica las flores y los frutos salen en grupos de 2-5. LK boropa Alibertia dwyeri LK2 tiene hojas muy parecidas, pero en A. dwyeri las estípulas son acostilladas y los frutos son de mayor tamaño. Usos: La madera es empleada en la fabricación de tajonas y mangos de herramientas. Los frutos maduros son comestibles y la pulpa es de sabor agradable, pero escasa. |
|
|
|